






HVAC Calculator Lite

Description of HVAC Calculator Lite
HVAC Calculator allows performing different calculations for HVAC systems engineering.
The program is a complex, unique by its size and content, comprising <b>30</b> calculations, vital for any HVAC engineer.
Now all the most up-to-date calculations are readily available for you, perform calculations anywhere: at a construction site, in negotiating, in a transport, office, auditorium etc.
You can select <b>Imperial</b> or <b>Metric</b> units in the program.
This program is also available <b>online for PC</b>: http://www.softhvac.com/hvac-calculator
Pro version contains <b>70</b> types of calculations, whereas Lite has got <b>30</b>.<br/></br></br></br></br></br></br>
<b>LIST OF FUNCTION:</b>
<b>Aerodynamics</b>
• Air velocity in terms of diameter.
• Air velocity in terms of dimensions.
• Air flow in terms of diameter.
• Air flow in terms of dimensions.
• Friction pressure drop in the circular duct.
• Friction pressure drop in the rectangular duct.
• Pressure drop in terms of local losses.
<b>Hydraulics</b>
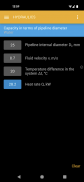
• Fluid velocity.
• Fluid flow in terms of diameter.
• Capacity in terms of diameter.
• Pipeline frictional pressure drop.
• Pressure drop in terms of local losses.
• Valve pressure drop.
<b>Heating</b>
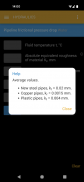
• Internal face temperature of the guarding.
• Single material guarding heat transmission resistance.
<b>Ventilation</b>
• Capacity for air heating.
• Air flow in terms of heat emission.
• Air flow in terms of humidity exudation.
<b>Air properties</b>
• Moisture content in the air in terms of enthalpy.
• Moisture content in the air in terms of relative humidity.
• Air enthalpy in terms of moisture content.
• Air enthalpy in terms of relative humidity.
• Air relative humidity in terms of moisture content.
• Air relative humidity in terms of enthalpy.
<b>Water properties</b>
• Water density.
• Water specific heat.
• Water kinematic viscosity.
<b>Engineering geometry</b>
• Steel pipeline weight.
• Surface area of the circular duct.
• Surface area of the rectangular duct.
<b>ADDITIONAL FUNCTIONS OF PRO VERSION:</b>
<b>Aerodynamics</b>
• Mass air flow rate.
• Volume air flow rate.
• Selection of the duct diameter.
• Selection of the rectangular duct dimensions.
• Circular orifice diameter.
• Circular orifice dimensions.
• Air velocity in terms of area.
• Air flow in terms of area.
<b>Hydraulics</b>
• Fluid flow in terms of capacity.
• Capacity in terms of fluid flow.
• Selection of the pipeline diameter in terms of flow.
• Selection of the pipeline diameter in terms of capacity.
• Throttling orifice diameter.
• Valve Kv
• System volume change.
• Pipeline thermal extension.
<b>Heating</b>
• Two materials guarding heat transmission resistance.
<b>Ventilation</b>
• Air cooling capacity by coil temperature.
• Air cooling capacity by relative humidity.
• Air cooling capacity by enthalpy.
• Fan electric motor capacity.
• Available pressure for natural ventilation.
• Water flow for air steam humidification.
• Capacity for air steam humidification.
<b>Air properties</b>
• Air mixture temperature.
• Air mixture moisture content.
• Air mixture enthalpy.
• Air mixture relative humidity.
• Steam saturation pressure in terms of temperature.
• Steam saturation pressure in terms of moisture content.
• Barometric pressure.
• Partial pressure.
• Dewpoint temperature.
• Air density.
• Air specific heat.
• Wet bulb temperature by relative humidity.
• Wet bulb temperature by enthalpy.
<b>Engineering geometry</b>
• Surface area of the circular section insulation.
• Surface area of the rectangular section insulation.
• Equivalent diameter.</br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br>
</br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br></br>
</br>
























